
Audiometry revealed significant mixed hearing loss in the right ear ( Figure 1B). On the day his hearing loss began, he recalled turning the CPAP up to the maximum allowed setting.Īudiograms were performed and compared with baseline audiograms performed in 2007 ( Figure 1A). Further questioning revealed a history of weight gain and subjective improvement in his OSA symptoms as he systematically increased the pressure on his CPAP machine.

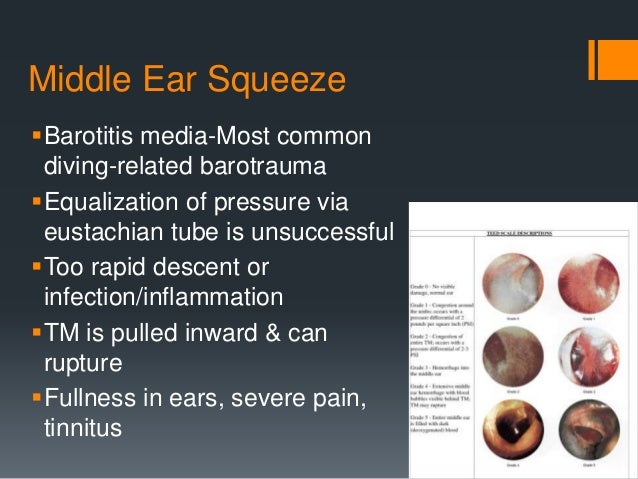
During examination, no perforation of the tympanic membrane was observed however, there was evidence of a significant clear serous effusion. He also reported sudden onset tinnitus but denied any symptoms of vertigo. The patient was seen intermittently during the next 4 years until 2011, when he presented to the clinic with a 1-week history of sudden hearing loss with the sensation of aural fullness, pain, and a pop sound in the right ear that had begun suddenly after excessive self-titration of CPAP. Snoring and apneic events were eliminated at a pressure of 15 cm H 2O. The patient subsequently underwent a CPAP titration study. He had never been titrated for CPAP therapy and had returned to the clinic at this time because of worsening symptoms. Polysomnography at the time of diagnosis revealed an apnea-hypopnea index of 57.5 with oxygen desaturations to 84%. He reported that in 2005 he was diagnosed with OSA. 3 We present a case of otic barotrauma resulting from excessive self-titration of CPAP in an in-home setting.Ī 50-year-old obese male presented in 2007 with a concern of snoring. 2Īdverse effects from CPAP use are numerous and most commonly include congestion, dryness of the oral and nasal cavities, aerophagia, epistaxis, sneezing, and sinusitis. The goal of the titration study is to establish the minimal pressure at which snoring ceases and apneic or hypopneic events are absent.
Barotrauma otic manual#
The pressure required for individual patients is variable and is determined by careful manual titration of pressures during a CPAP titration study. 2 CPAP prevents the collapse of the upper airway by providing continuous positive pressure to the oropharynx and nasopharynx. The traditional treatment for patients with OSA is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). This collapse causes the characteristic apneic or hypopneic events that define the diagnosis of OSA. The pathophysiology of OSA is postulated to be related to decreased parasympathetic activity during sleep, leading to decreased muscle tone in the upper airway that can in turn lead to repetitive collapse of the upper airway. 1 Throughout the years, this number has consistently increased, possibly secondary to the rising prevalence of obesity in the population. Some form of OSA affects approximately 17% of the adult population. Sensorineural hearing loss or vertigo during descent suggests the development of a perilymph fistula the same symptoms during ascent from a deep-sea dive can additionally suggest an air bubble formation in the inner ear.Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common yet underrecognized condition. read more ) or descent (eg, during air travel).

It can affect the ear (causing ear pain, hearing loss, and/or vestibular symptoms) or the sinuses. Symptoms usually worsen during rapid increase in external air pressures, such as a rapid ascent (eg, during scuba diving Ear and Sinus Barotrauma Barotrauma is tissue injury caused by a pressure-related change in body compartment gas volume. read more and/or vertigo Dizziness and Vertigo Dizziness is an imprecise term patients often use to describe various related sensations, including Faintness (a feeling of impending syncope) Light-headedness Feeling of imbalance or unsteadiness. More than 10% of people in the US have some degree of hearing loss that compromises their. Symptoms of otic barotrauma are severe pain, conductive hearing loss, and, if there is a perilymph fistula, sensorineural hearing loss Hearing Loss Worldwide, about half a billion people (almost 8% of the world's population) have hearing loss ( 1).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
